Authentication
Setup
This section is dedicated to authenticate and authorize users to avail support chat in your android app. You can also get instruction to set and update user details such as pre-chat lead collection forms to get user's information before starting the chat, updating user details of an existing user and sending additional details as metadata along with user details.
Get your APP_ID
Sign up for Kommunicate to get your APP_ID. You will get the APP_ID from the Install section. This APP_ID is used to create/launch conversations.
Initialize SDK
After the Gradle sync is finished with Kommunicate dependency, you can initialize the SDK by calling the below method:
Kommunicate.init(context, APP_ID);
You can initialize the SDK in onCreate() function of your Activity. Just make sure it is initialized before accessing any method from the Kommuniate SDK.
The APP_ID parameter will take the application id(APP_ID) you just acquired.
For the context parameter you can pass the application context using the getApplicationContext() method. However if you are unable to get that, you can also pass the activity context: YourActivityName.this
Registration/Login
1. Visitors
You might not have the details of all the users coming to chat. You can start the chat with a visitor by calling the below method from the SDK:
Kotlin
If you are using Kotlin:
Kommunicate.loginAsVisitor(this, object : KMLoginHandler {
override fun onSuccess(registrationResponse: RegistrationResponse, context: Context) {
// You can perform operations such as opening the conversation, creating a new conversation or update user details on success
}
override fun onFailure(
registrationResponse: RegistrationResponse,
exception: Exception
) {
// You can perform actions such as repeating the login call or throw an error message on failure
}
})
Java
If you are using Java:
Kommunicate.loginAsVisitor(this, new KMLoginHandler() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(RegistrationResponse registrationResponse, Context context) {
// You can perform operations such as opening the conversation, creating a new conversation or update user details on success
}
@Override
public void onFailure(RegistrationResponse registrationResponse, Exception exception) {
// You can perform actions such as repeating the login call or throw an error message on failure
}
});
2. Pre chat Lead Collection
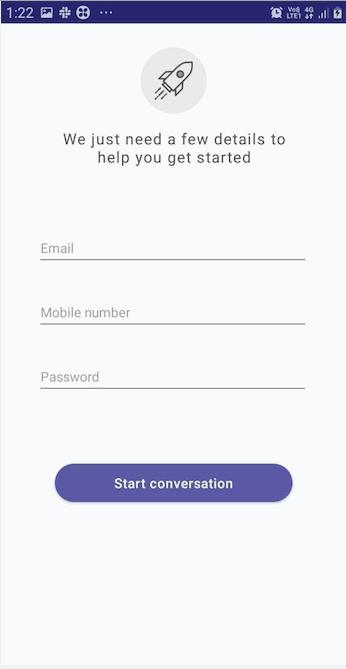
There are 2 ways you can create pre-chat lead collection for your users.
1. Create fields from dashboard
If you wish to use this method, the prechat lead collection will be identical throughout all platform.
You can create the fields from here. After creating the fields, you can use this code in your application:
Kotlin
If you are using Kotlin:
val progressDialog = ProgressDialog(context).apply {
setTitle("Logging in..")
setMessage("Please wait...")
setCancelable(false)
show()
}
Kommunicate.launchConversationWithPreChat(context, progressDialog, object : KmCallback {
override fun onSuccess(message: Any) {
finish()
progressDialog.dismiss()
}
override fun onFailure(error: Any) {
progressDialog.dismiss()
}
})
Java
If you are using Java:
final ProgressDialog progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(YourActivityName.this);
progressDialog.setTitle("Logging in..");
progressDialog.setMessage("Please wait...");
progressDialog.setCancelable(false);
progressDialog.show();
Kommunicate.launchConversationWithPreChat(YourActivityName.this, progressDialog, new KmCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Object message) {
finish();
progressDialog.dismiss();
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Object error) {
progressDialog.dismiss();
}
});
Replace YourActivityName.this with your own Activity name.
2. Set custom fields in Pre-chat lead collection form
We support adding custom fields in pre-chat lead form, the field types currently supported are email, text, number, password and dropdown. If you are creating fields from dashboard, this method is not required.
Follow these steps to create your own custom fields:
- Create a list of KmPreChatInputModel which will contain the list of fields which are to be shown to user. Example: Email, Phone number.
- Pass this list to
Kommunicate.launchPrechatWithResult(YourActivityName.this, `<list>`, KmPrechatCallback) KmPrechatCallbackwill return you the data which user entered in Lead collection.- Use this data to create new conversation for the user.
Kotlin
If you are using Kotlin:
val inputModelList: MutableList<KmPrechatInputModel> = mutableListOf()
val emailField = KmPrechatInputModel().apply {
this.type = KmPrechatInputModel.KmInputType.EMAIL
this.isRequired = true
this.placeholder = "Enter email"
this.validationRegex = EMAIL_VALIDATION_REGEX //create static value for email regex
this.field = "Email" //This will be returned as key
this.compositeRequiredField = "Phone" //optional: "Either Phone or Email is required" if you set another field as composite field
}
val nameField = KmPrechatInputModel().apply {
this.type = KmPrechatInputModel.KmInputType.TEXT
this.placeholder = "Enter Name"
this.field = "Name"
}
val contactField = KmPrechatInputModel().apply {
this.type = KmPrechatInputModel.KmInputType.NUMBER
this.placeholder = "Enter Phone number"
this.field = "Phone"
this.validationRegex = PHONE_NUMBER_VALIDATION_REGEX
}
val dropdownField = KmPrechatInputModel().apply {
this.options = mutableListOf("Male", "Female") //list of options to show
this.placeholder = "Enter your gender"
this.field = "Gender"
this.element = "select" //element must be "select" for dropdown menu
}
inputModelList.add(emailField)
inputModelList.add(nameField)
inputModelList.add(contactField)
inputModelList.add(dropdownField)
Kommunicate.launchPrechatWithResult(
context = this,
inputModelList = inputModelList,
callback = object : KmPrechatCallback<Map<String, String>> {
override fun onReceive(
data: Map<String, String>,
context: Context,
finishActivityReceiver: ResultReceiver
) {
Utils.printLog(
context, "TestPrechat", GsonUtils.getJsonFromObject(
data,
MutableMap::class.java
)
)
val user = KMUser().apply {
if (!data["Email"].isNullOrEmpty()) {
userId = data["Email"]
email = data["Email"]
}
if (!data["Phone"].isNullOrEmpty()) {
contactNumber = data["Phone"]
}
if (!data["Name"].isNullOrEmpty()) {
displayName = data["Name"]
}
if (!data["Gender"].isNullOrEmpty()) {
metadata = mapOf(
"Gender" to data["Gender"]
)
}
}
KmConversationBuilder(context).apply {
kmUser = user
launchConversation(object : KmCallback {
override fun onSuccess(message: Any) {
finishActivityReceiver.send(
KmConstants.PRECHAT_RESULT_CODE,
null
) //To finish the Prechat activity
Log.d("Conversation", "Success : $message")
}
override fun onFailure(error: Any) {
finishActivityReceiver.send(
1000,
null
) //To dismiss the loading progress bar
Log.d("Conversation", "Failure : $error")
}
})
}
}
override fun onError(error: String) {
Utils.printLog(
context, "TestPrechat",
"Error : $error"
)
}
})
Java
If you are using Java:
List<KmPrechatInputModel> inputModelList = new ArrayList<>();
KmPrechatInputModel emailField = new KmPrechatInputModel();
emailField.setType(KmPrechatInputModel.KmInputType.EMAIL);
emailField.setRequired(true);
emailField.setPlaceholder("Enter email");
emailField.setValidationRegex(EMAIL_VALIDATION_REGEX); //create static value for email regex
emailField.setField("Email"); //This will be returned as key
emailField.setCompositeRequiredField("Phone"); //optional: "Either Phone or Email is required" if you set another field as composite field
KmPrechatInputModel nameField = new KmPrechatInputModel();
nameField.setType(KmPrechatInputModel.KmInputType.TEXT);
nameField.setPlaceholder("Enter Name");
nameField.setField("Name");
KmPrechatInputModel contactField = new KmPrechatInputModel();
contactField.setType(KmPrechatInputModel.KmInputType.NUMBER);
contactField.setPlaceholder("Enter Phone number");
contactField.setValidationRegex(PHONE_NUMBER_VALIDATION_REGEX);
contactField.setField("Phone");
KmPrechatInputModel dropdownField = new KmPrechatInputModel();
dropdownField.setOptions(Arrays.asList("Male", "Female")); //list of options to show
dropdownField.setPlaceholder("Enter your gender");
dropdownField.setField("Gender");
dropdownField.setElement("select"); //element must be "select" for dropdown menu
inputModelList.add(emailField);
inputModelList.add(nameField);
inputModelList.add(contactField);
inputModelList.add(dropdownField);
Kommunicate.launchPrechatWithResult(MainActivity.this, inputModelList, new KmPrechatCallback<Map <String, String>>() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Map < String, String > data, Context context, final ResultReceiver finishActivityReceiver) {
Utils.printLog(context, "TestPrechat", GsonUtils.getJsonFromObject(data, Map.class));
KMUser user = new KMUser();
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(data.get("Email"))) {
user.setUserId(data.get("Email"));
user.setEmail(data.get("Email"));
}
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(data.get("Phone"))) {
user.setContactNumber(data.get("Phone"));
}
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(data.get("Name"))) {
user.setDisplayName(data.get("Name"));
}
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(data.get("Gender"))) {
Map<String, String> metaData = new HashMap<>();
metaData.put("Gender", data.get("Gender")); // other metadata can be added accordingly
user.setMetadata(metaData);
}
new KmConversationBuilder(MainActivity.this)
.setKmUser(user) //this is important to login the user
.launchConversation(new KmCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Object message) {
finishActivityReceiver.send(KmConstants.PRECHAT_RESULT_CODE, null); //To finish the Prechat activity
Log.d("Conversation", "Success : " + message);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Object error) {
finishActivityReceiver.send(1000, null); //To dismiss the loading progress bar
Log.d("Conversation", "Failure : " + error);
}
});
}
@Override
public void onError(String error) {
Utils.printLog(MainActivity.this, "TestPrechat", "Error : " + error);
}
});
Replace YourActivityName.this with your activity name. Search for "testPrechat" in your logchat after entering the values in prechat to see the data.
3. Registered User
If you already have your user's detail, there are 2 ways you can log in the user:
- When you authenticate the user in your app, then login the user to Kommunicate as well. This method is more effective in terms of performance.
You can authorize a user by using the below method:
Kotlin
If you are using Kotlin:
val user = KMUser().apply {
userId = <USER_ID>
}
Java
If you are using Java:
KMUser user = new KMUser();
user.setUserId(<USER_ID>); // You can set any unique user ID
Post this, call the method as described below:
Kotlin
If you are using Kotlin:
Kommunicate.login(this, user, object : KMLoginHandler {
override fun onSuccess(registrationResponse: RegistrationResponse, context: Context) {
// You can perform operations such as opening the conversation, creating a new conversation or update user details on success
}
override fun onFailure(
registrationResponse: RegistrationResponse,
exception: java.lang.Exception
) {
// You can perform actions such as repeating the login call or throw an error message on failure
}
})
Java
If you are using Java:
Kommunicate.login(this, user, new KMLoginHandler() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(RegistrationResponse registrationResponse, Context context) {
// You can perform operations such as opening the conversation, creating a new conversation or update user details on success
}
@Override
public void onFailure(RegistrationResponse registrationResponse, Exception exception) {
// You can perform actions such as repeating the login call or throw an error message on failure
}
});
You can also add other optional custom fields such as emails, display name, contact number etc. to the user object:
Kotlin
If you are using Kotlin:
user.apply {
displayName = <DISPLAY_NAME> // Pass the display name of the user
password = <PASSWORD>
imageLink = <IMAGE_URL> // Pass the image URL for the user's display image
contactNumber = <PHONE_NUMBER> // Pass the user's contact number
email = <EMAIL_ID> // Pass the email ID of the user
}
Java
If you are using Java:
user.setDisplayName(<DISPLAY_NAME>); // Pass the display name of the user
user.setPassword(<PASSWORD>);
user.setImageLink(<IMAGE_URL>); // Pass the image URL for the user's display image
user.setContactNumber(<PHONE_NUMBER>); // Pass the user's contact number
user.setEmail(<EMAIL_ID>); // Pass the email ID of the user
If you want to get the user details of the logged in user, use this code snippet:
Kotlin
If you want to use Kotlin:
val user = KMUser.getLoggedInUser(context)
Java
If you want to use Java:
KMUser user = KMUser.getLoggedInUser(context);
- You can login the user when conversations are created/launched using KmConversationBuilder
If you already have the user details then create a KMUser object using the details and launch the conversation. Use the builder as below to create KMUser object with already existing details:
Kotlin
If you are using Kotlin:
val user = KMUser().apply {
userId = <USER_ID> // Pass the display name of the user
password = <PASSWORD>
imageLink = <IMAGE_URL> // Pass the image URL for the user's display image
displayName = <DISPLAY_NAME>
}
Java
If you are using Java:
KMUser user = new KMUser();
user.setUserId(<USER_ID>); // Pass a unique key
user.setPassword(<PASSWORD>); //Optional
user.setImageLink(<IMAGE_URL>); // Optional
user.setDisplayName(<DISPLAY_NAME>); //Optional
Then pass this user object to the setKmUser method as below:
Kotlin
If you are using Kotlin:
KmConversationBuilder(activityContext)
.setKmUser(user)
.launchConversation(object : KmCallback {
override fun onSuccess(message: Any) {
Log.d("Conversation", "Success : $message")
}
override fun onFailure(error: Any) {
Log.d("Conversation", "Failure : $error")
}
})
Java
If you are using Java:
new KmConversationBuilder(activityContext)
.setKmUser(user)
.launchConversation(new KmCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(Object message) {
Log.d("Conversation", "Success : " + message);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Object error) {
Log.d("Conversation", "Failure : " + error);
}
});
For the activityContext parameter you need to pass the activity context. One way to get it is the YourActivityName.this.
Pass additional details as metadata
Sometimes, you may need to pass additional details for the user apart from the already existing properties of KMUser. You can pass the additional details in metadata of the KMUser object. Your team will see this data in dashboard.
Kotlin
If you are using Kotlin:
val metadata: Map<String, String> = mapOf(
"Department" to "Engineering", // This is example data. You can set it according to the additional details you want to add
"Designation" to "Software Engineer",// This is example data
"Team" to "Device Team" // This is example data
)
kmUser.metadata = metadata
Java
If you are using Java:
Map<String, String> metadata = new HashMap<>();
metadata.put("Department" , "Engineering"); // This is example data. You can set it according to the additional details you want to add
metadata.put("Designation" , "Software Engineer"); // This is example data
metadata.put("Team" , "Device Team"); // This is example data
kmUser.setMetadata(metadata);
Check if logged in
You do not need to login the user everytime so you can do a check before logging in the user if the user is already logged in. This method returns a boolean value.
KMUser.isLoggedIn(context)
Update the details of logged in users
Once the user has logged in, you can still update some of their properties such as display name, image Url, contact number, metadata, and status.
First, create a KMUser object and set the property you want to update:
Kotlin
If you are using Kotlin:
val kmUser = KMUser().apply {
displayName = <NEW_DISPLAY_NAME>
imageLink = <NEW_IMAGE_URL>
metadata = mapOf(
"Department" to "Mobility", // This is an example of updating metadata.
"Designation" to "Software Engineer II" // This is an example of updating metadata.
)
}
Java
If you are using Java:
KMUser kmUser = new KMUser();
kmUser.setDisplayName(<NEW_DISPLAY_NAME>);
kmUser.setImageLink(<NEW_IMAGE_URL>);
Map<String, String> metadata = new HashMap<>();
metadata.put("Department" , "Mobility"); // This is an example of updating metadata.
metadata.put("Designation" , "Software Engineer II"); // This is an example of updating metadata.
kmUser.setMetadata(metadata);
Then call the below method in a background thread or Async task:
UserService.getInstance(context).updateLoggedInUser(kmUser);
